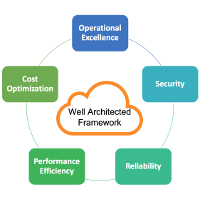
Amazon Well Architected Framework and its 5 Pillars
Posted on 05 Feb 2021
In this article, I will talk about the Amazon Well-Architected Framework. This is a set of best practices to help customers design their software solutions.
The Amazon WAF is a set of best practices to help customers to create secure, efficient, cost-effective, and reliable solutions for their businesses. The framework started as a simple whitepaper that expanded to include domain-specific lenses, hands-on labs, and tools. Therefore, the basic idea is to have mechanisms for regularly evaluating your workloads, identifying high-risk issues, and find room for improvements.
The framework leverages five main pillars:
- Security
- Reliability
- Performance efficiency
- Cost optimization
- Operational excellence

Photo from https://www.reply.com/
Each Pillar follows a list of design principles that apply in a set of areas. Let’s analyze them in the next sections.
Amazon Well-Architected Framework Security Pillar
Security is one of the most important aspects of the Amazon Cloud platform. In fact, AWS guarantees the protection of your data and infrastructure to prevent unauthorized usage and access.
Security Design Principles
Amazon AWS to secure its environments leveraging the following design principles:
- Apply security at all layers. An Amazon’s customer cloud environment has several infrastructure layers like network, file storage, VM, database, object storage, and others. The platform implements security facilities in all these layers allowing the customer to protect its data and infrastructure from unauthorized access and usage.
- Enable traceability of security events. AWS monitors every action in the customer infrastructure with logs and metrics that are available for audit and analysis at whatever moment.
- Implement a strong identity foundation. AWS platform uses the principle of least privilege and enforces separation of duties with the appropriate authorization for each interaction with your AWS resources.
- Automate security best practices. It is important to automate the security mechanisms in order to improve the ability to scale more rapidly and cost-effectively. This automation is basically the implementation of version-controlled code containing all the necessary elements to secure data and the infrastructure.
- Protect data in transit and at rest. Use sensitivity levels to classify your data and use mechanisms, such as encryption, tokenization, and access control where appropriate.
- Keep people away from data. The idea is to use mechanisms and tools to avoid direct access to data and their manipulation. The goal is to reduce the risk of human error when handling sensitive data.
- Prepare for security events. Define processes and policies for incident management and investigation. Moreover, run incident response simulations, and use tools to increase your speed for detection, investigation, and recovery.
Five Security Areas
The above design principles apply in the following five security areas:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM). It is the tool that Amazon uses to know who access to a system and if he is entitled to access the resources. Basically, the tools manage authentication and access management to AWS resources. You can set up advanced identity mechanisms like SSO and strong Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and use permission to grant access to the resources
- Detective Controls. It is the ability of the Amazon platform to detect security issues, threats, or unexpected behavior. In addition, it helps in legal and certification compliance because it finds gaps between the actual configuration and the one expected. AWS uses different methods to identify security incidents like, for example, the log analysis to detect unauthorized access. In general, customers can configure different AWS services to activate these controls, when an issue is found there are tools (i.e. playbooks, runbook, etc.) that help them to solve it.
- Infrastructure protection. This area helps customers to protect systems and services in their infrastructure from unintended and unauthorized access. It also protects against potential vulnerabilities. All these protection goes into two main categories: Network and Compute Protections.
- Data protection. This area is related on how customer protects their data. There are different ways to achieve this goal. For example, data classification helps a customer to classify data for importance and define who can access what data. Another way to protect data is encryption and tokenization. In the disaster recovery scenario, backup and restore are the methods to use, while for high availability the replication is the way to go.
- Incident Response. Even with the more advanced security prevention system a customer needs a process to respond to the security incidents, assess the issues, and mitigate the risks.
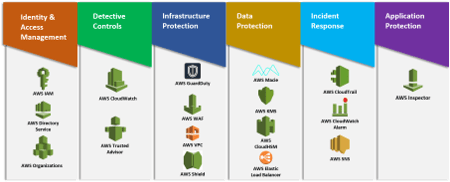
Photo from https://dzone.com
Amazon Well-Architected Framework Reliability Pillar
This pillar makes sure that customer workload runs correctly and consistently even when a failure occurs in the system.
Reliability Design Principles
Amazon AWS runs reliable workloads leveraging the following design principles:
- Automatically recover from failure. The platform provides a mechanism to recover from failure and continue to provide services to the end-users. For example, in the following article, we talked about load balancers as a mechanism to detect an EC2 system failure and redirect traffic to another EC2 instance.
- Test recovery procedures. In the Cloud, you can simulate system failure in order to test and validate the recovery strategies.
- Scale horizontally to increase aggregate workload availability. In the previous article, we already talked about the platform’s ability to add redundancies to satisfy a capacity increase in the workload.
- Stop guessing capacity. In the On-Premis world, customers need to plan in advance the system capacity. However, this translates to underutilization or overconsume of the system resources. The Cloud system resolves this issue by starting to use minimal resources and add new capacity on the fly based on requests.
- Manage change in automation. In a typical On-Premis environment when something bad occurs in the system administrators or operators resolve them manually. This is unfeasible in a reliable system where changes must only be applied with automation. Add fixes in automation require more time but it has a lot of benefits like reproducibility, traceability, versioning of changes, and so on.
The reliability of a system depends on several factors, the primary of which is Resiliency.
Resiliency is the ability of a workload to recover from infrastructure or service disruptions (Disaster Recovery), dynamically acquire computing resources to meet demand (Scalability), and mitigate disruptions, such as misconfigurations or transient network issues (Availability). In the official Amazon documentation, you can find the different metrics to measure the Availability and Disaster Recovery efficiency of a system.
Three Reliability Areas
Reliability in the Amazon Cloud focuses on three areas:
- Foundations. When you design a system you have to design it with Reliability in mind. You should take into account redundancy to meet Availability requirements. You have to think about what happens if suddenly the whole system crash and all data are lost. How do you put in place the system again? How do you recover the data? Basically, you have to think about how to guarantee Business Continuity even when a disaster occurs. Finally, you have to design your system to avoid extra costs due to unused capacity and, at the same time, that this capacity fits the requirement every time.
- Change Management. When you design a system you should start immediately to think about how do you patch it. Patching is a critical aspect of software design and it should be taken into account as soon as possible. In addition, you also have to take into consideration how this change affects the system.
- Failure Management. When you design your system you have to take into account that failures are not a rare event. Failures are always possible and your design should anticipate what failure can occur and how do you recover from them.
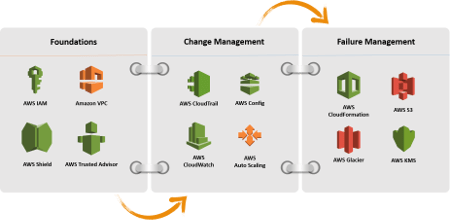
Photo from https://dzone.com
Amazon Well-Architected Framework Performance Efficiency Pillar
This Pillar focuses on ensuring a system delivers maximum performance efficiency. In order to do that, you should follow the following design principles.
The Five Performance Efficiency Design Principles
The following are the design principles you can use to achieve performance efficiency:
- Democratize Advanced Technologies. Modern technologies can help you to architect complex scenarios easily, however, you need an IT team to manage this complexity. Using the Cloud you leave this complexity the Cloud provider and you just consume these technologies as a service.
- Go Global in Minutes. As described in the following article AWS has 24 regions and 77 Availability Zones (AZ) so you can go global in minutes. Therefore, you can deploy your application close to your audience using also services like CloudFront. In this way, you can reduce latency improving user experience, and leveraging on the economy of scale to minimize costs.
- Use Serverless Architectures. Reduce overhead of running and maintaining servers and use the available AWS options to host and monitor infrastructure.
- Experiment more often. With a virtual and automated system and deployment, it is very easy to test the system and infrastructure with different types of instances, storage, or configurations.
- Have mechanical sympathy. This principle suggests that you use the technology approach that best aligns with what you are trying to achieve.
The Four Performance Efficiency Areas
The above design principles are applicable in the following areas:
- Select customizable solutions. The customer needs to start with the right architecture and configuration for his workload. He should anticipate possible changes in the configuration if workload variations can occur during the system lifecycle.
- Review to continually innovate. You have to continuously review how AWS resources respond to your workload in order to adjust the configuration and take advantage of new technology that every day will be available and that could improve the performance efficiency.
- Monitor AWS services. The review should be based on real data and not on a hypothesis, for this reason, the system must be continuously monitored in order to find-out performance inefficiency and find the right solution to the issue. AWS makes available tools like CloudWatch, Kinesis, etc.
- Consider the trade-offs. An example of a trade-off that ensures an optimal approach is trading consistency, durability, and space versus time or latency to ensure that you deliver high performance.
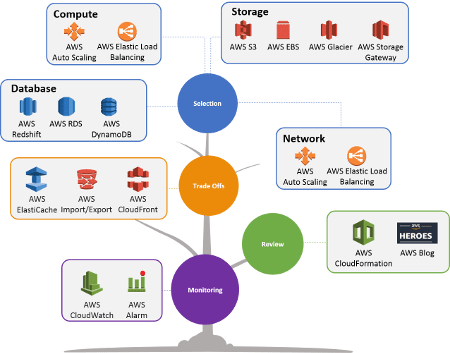
Photo from https://dzone.com
Amazon Well-Architected Framework Cost Optimization Pillar
The goal of this Pillar is to make aware the customer of AWS resource costs and find ways to optimize them.
The Six Cost Optimization Design Principles
- Adopt a Consumption Model. The basic idea is to pay only for the AWS resources that you consume. In fact, your workload can increase or decrease and you can adapt your infrastructure to it without a capacity plan and without under-consume or overconsume resources.
- Measure Overall Efficiency. You can adapt your infrastructure to your workload increasing or decreasing the capacity only if you measure it. Measures allow you to understand in every moment how your infrastructure reacts to your workload and this allows you to understand how to adapt over time.
- Reduce Spending on Data Center Operations. The Responsibility model of the Cloud platform allows you to avoid spending time and energy to buy and maintain servers, networking, power, disks. In fact, it let the Cloud provider take the responsibility to manage them so you can focus on your business. A large economy of scale allows you to have the resource you need at a lower cost.
- Analyze and Attribute Expenditure. AWS allows you to easily identify how many resources your business consumes, you can easily breakdown these costs and analyze them for better asset allocation.
- Use Managed Services. Managed services can help your business to reduce costs. If you have an Ec2 instance running an eCommerce website where you manage the database by yourself you can decide that using Amazon RDS service can reduce costs for deployment and maintain it, provide automatic backups for disaster recovery, and so on. If you manage your Newsletter by yourself using open source software, you can decide to use Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) to avoid all the complexity to manage a reliable email sender.
The Four Cost Optimization Areas
The above design principles are applicable in the following areas:
- Use cost-effective resources. Customers must use the right resources and configuration that help to meet the requirements. For each AWS resource customers will know its impact on the overall cost.
- Matching supply with demand. AWS helps customers to rapidly change the resource availability as the workload and requirement changes. Components like auto-scaler in combination with a monitoring tool like CloudWatch help to resize the infrastructure as per requirement.
- Increase expenditure awareness. Amazon platform allows the customer to know in every moment the overall cost of the whole infrastructure, the breakdown for each resource, and how they impact the costs currently and in the future. This allows us to keep track of costs and plan for the future.
- Optimize over time. The awareness of the overall costs and their breakdown for all the resources used allows customers to keep track of these costs and find ways to optimize them.
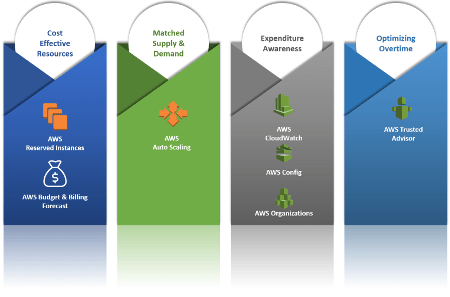
Photo from https://dzone.com
Amazon Well-Architected Framework Operation Excellence Pillar
The Operational Excellence Pillar focuses on running and monitoring systems to deliver business value in continually improving processes and procedures for you. It is important to understand that a project does not end when it is first installed in production. On the contrary, that is his first day of life. From that day on, you have to monitor your infrastructure and application to understand how it reacts to workloads and how to continuously improve things. To do that we need to work with the following design principles in mind.
Operation Excell Design Principles
- Make frequent, small, reversible changes. Bug in code is inevitable, but to avoid transforming the patching process in a cumbersome apply changes in small size increments on a regular interval.
- Perform operations as code. Do not apply these changes manually but define a process to automatically apply them.
- Anticipate failure. If bugs are inevitable, failures occur more often than you think. Therefore, design your application knowing that failure occurs at every moment, create tests with pre-defined failure scenarios to understand its impact.
- Annotate documentation: Automate documentation on every build which can be used by systems and humans.
- Refine operations procedures often: As operations procedures are designed, we should keep checking and evaluating the process for the latest updates.
- Learn from all operational failures: Keep track of all failures and events. If you think part of the application must be fixed, do it. Moreover, try to understand how customers use your application and use this knowledge to fix issues, simplify design, design new features that help customers to use your application better.
Operation Excell three areas
Apply the above design principles in the following three areas:
- Manage and automate changes (Prepare). Create pipeline codes to modify your code in the development, test, and production environment.
- Respond to events. When your application is in productions event happens at every moment. In fact, failures and change requests are some examples of these events. For this reason, you need to define a process to respond to these events.
- Define the standards. A process is not enough to manage an application in production. You need to define standards to avoid that each operator works on their own and that everyone does what he likes.
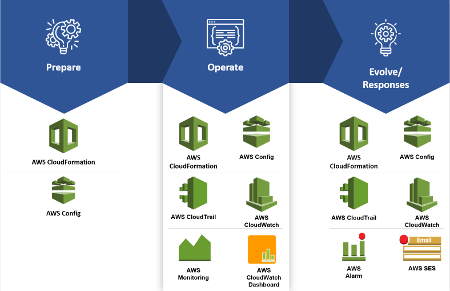
Photo from https://dzone.com
Conclusion
In conclusion, in this article, we analyzed the Amazon Well-Architected Framework, a set of best practices to help you to design secure, reliable, efficient, and cost-effective applications for the Cloud. Consider these guidelines as a tool to help you to organize your infrastructure and data.


